XRS7000 series switches are integrated circuits (ICs) that add HSR, PRP and time synchronization functionality to your device. This chip series is the first off-the-shelf HSR/PRP Ethernet chip in the market and is part of Arrow Electronics’ SpeedChips product family.
Features
There are two different XRS7000 versions available: XRS7003 (three ports) and XRS7004 (four ports). XRS7003 can be employed in HSR and PRP End Nodes, while XRS7004 can be used in both HSR and PRP End Nodes and RedBoxes. A QuadBox can be built using two XRS7004 devices.
- Compatible with High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR)
- Compatible with Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP)
- Two (XRS7003) or three (XRS7004) 10/100/1000 Mbit/s RGMII ports
- Time and frequency synchronization using IEEE1588-2008 Precision Time Protocol v2
- I2C and MDIO for register access
- Cut-through and store-and-forward operation
- Quality of Services (QoS) with priority tagging, packet filtering and four priority queues per port
- Port-based VLAN and VLAN tagging
- PPS (Pulse per Second) input and output
- Support for MAC address based authenticating methods
- RMON statistics counters
- Two industrial range packages available: 144-Pin Plastic Enhanced Quad Flat Pack (EQFP) and 256-Pin Fine Line Ball Grid Array (FBGA)
Technologies
High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) is a standard (IEC 62439-3 Clause 5) fulfilling the need for reliable Ethernet. It is suitable for applications that require short reaction times and high availability. With HSR, a network can be made very robust with zero reaction time in case of a single failure, with predictable latency and with less cost than with other Ethernet redundancy solutions.
Many critical applications require a network with zero downtime. The network is fully operational even during maintenance, as any device can be disconnected and replaced without breaking the network connectivity. This makes the network very reliable and highly available.
Find out more on our technology page.
The Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) is an IEC standard (IEC 62439-3 Clause 4) providing redundant Ethernet. Under PRP, each node is connected to two separate parallel LANs, parallel Local Area Networks (LANs). Source nodes send two copies of each packet, one over each network. When a destination node receives a packet, it accepts the first copy and discards the second copy, eliminating the duplicate.
HSR is more cost-effective than PRP because HSR requires significantly less cabling. Therefore, HSR can be considered the most effective redundancy solution available for Ethernet at the moment.
Find out more on our technology page.
Configuration
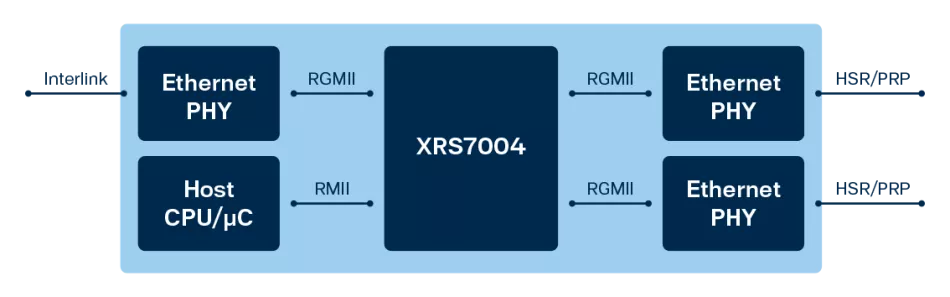
Below is an example of an HSR/PRP RedBox built using XRS7004
Technical Specifications
Feature |
XRS7003 | XRS7004 |
|---|---|---|
10/100/1000 Mbit/s RGMII ports |
2 | 3 |
10/100 Mbit/s RMII ports |
1 | 1 |
High-Availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) |
Yes | Yes |
Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) |
Yes | Yes |
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) |
Yes | Yes |
Queues per port |
4 | 4 |
Maximum number of VLANs |
4096 | 4096 |
Recommended HSR network size |
Up to 512 hops | Up to 512 hops |
HSR proxy node table size |
64 nodes | 512 nodes |
Package* |
144-Pin Plastic Enhanced Quad Flat Pack (EQFP) or 256-Pin Fine Line Ball Grid Array (FBGA) | |
Temperature range |
-40° C to +100° C | -40° C to +100° C |
| * The XRS7003 and XRS7004 are pin compatible with the exception of XRS7004 having one RGMII port more than XRS7003. | ||